Embark on a mathematical odyssey with Unit 2 Introducing Ratios Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unravels the intricacies of ratios, their applications, and their significance in various fields. This key unlocks the secrets of proportions, simplifies ratios, and unveils the diverse applications of ratios in science, engineering, and beyond.
Unit 2 delves into the fundamental concepts of ratios, empowering students to analyze and solve problems effectively. By exploring real-world scenarios and engaging practice exercises, this answer key transforms the learning of ratios into an enriching and practical experience.
Introduction

In mathematics, a ratio is a comparison of two quantities. Ratios are used to express the relative sizes of two quantities, and they can be used to solve a variety of problems.
There are different types of ratios, including:
- Ratios of whole numbers:These ratios are expressed as fractions, such as 3:4 or 5:7.
- Ratios of decimals:These ratios are expressed as decimals, such as 0.5:0.75 or 1.25:1.5.
- Ratios of fractions:These ratios are expressed as fractions, such as 1/2:2/3 or 3/4:5/6.
Ratios are used in a variety of real-world scenarios, such as:
- Cooking:Ratios are used to determine the correct proportions of ingredients in a recipe.
- Construction:Ratios are used to determine the correct proportions of materials in a mixture, such as concrete or paint.
- Finance:Ratios are used to compare the financial performance of different companies.
Unit 2: Introducing Ratios
Unit 2 of the mathematics curriculum introduces the concept of ratios and their applications. It builds upon the foundational understanding of fractions and proportions, extending students’ knowledge to compare and interpret relationships between quantities.
Key Concepts Covered in Unit 2, Unit 2 introducing ratios answer key
Unit 2 covers several key concepts related to ratios:
- Definition of a ratio:A ratio is a comparison of two quantities, expressed as a fraction or quotient.
- Equivalent ratios:Ratios that represent the same relationship between quantities, even if they are expressed in different forms.
- Simplifying ratios:Reducing ratios to their simplest form by dividing both numerator and denominator by a common factor.
- Solving ratio problems:Using ratios to solve problems involving proportional relationships between quantities.
- Applications of ratios:Ratios are used in various real-world contexts, such as mixing ingredients in cooking, scaling recipes, and determining distances on maps.
Simplifying Ratios
Simplifying ratios is the process of reducing them to their lowest terms, which means expressing them in the simplest possible form. This makes it easier to compare ratios and to perform mathematical operations on them.
To simplify a ratio, we need to find the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator and then divide both the numerator and denominator by the GCF. The GCF is the largest number that divides evenly into both the numerator and denominator without leaving a remainder.
Finding the GCF
- Prime Factorization:Factor the numerator and denominator into prime numbers. The GCF is the product of the common prime factors.
- Listing Factors:List the factors of both the numerator and denominator. The GCF is the largest factor that is common to both lists.
- Euclidean Algorithm:This is a more efficient method that involves repeatedly dividing the larger number by the smaller number and taking the remainder. The last non-zero remainder is the GCF.
Examples of Simplifying Ratios
| Original Ratio | GCF | Simplified Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 12:18 | 6 | 2:3 |
| 20:24 | 4 | 5:6 |
| 36:48 | 12 | 3:4 |
Solving Proportions
Proportions are equations that state that two ratios are equal. They are often used to solve problems involving ratios, such as finding the missing value in a ratio or determining whether two ratios are equivalent.
Step-by-Step Guide to Solving Proportions
- Cross-multiply the numerators and denominators of the two ratios.
- Set the products equal to each other and solve for the unknown variable.
Practice Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the value of x in the proportion 2/5 = x/10 | x = 4 |
| Determine whether the ratios 3/4 and 9/12 are equivalent | Yes, the ratios are equivalent because 3/4 = 9/12 |
Applications of Ratios
Ratios are used in various fields to compare quantities and solve problems. In science, ratios are used to represent the concentrations of chemicals in solutions, the proportions of different elements in compounds, and the relationships between physical quantities such as mass, volume, and density.
In engineering, ratios are used to design structures, machines, and systems. For example, the ratio of the length of a beam to its width determines its strength, and the ratio of the diameter of a pipe to its length determines its flow rate.
In finance, ratios are used to analyze the financial health of companies. For example, the debt-to-equity ratio measures the amount of debt a company has relative to its equity, and the current ratio measures a company’s ability to meet its short-term obligations.
Real-Life Examples
Here are some real-life examples where ratios are used:
- A doctor prescribes a medication in a ratio of 2:1, meaning that for every 2 units of the active ingredient, there is 1 unit of inactive ingredients.
- A baker uses a ratio of 3:2:1 for flour, sugar, and butter in a cake recipe.
- An architect designs a building with a height-to-width ratio of 2:1.
- A financial analyst calculates a company’s debt-to-equity ratio to assess its financial risk.
Professions that Commonly Use Ratios
Some professions that commonly use ratios include:
- Scientists
- Engineers
- Doctors
- Financial analysts
- Architects
- Chemists
- Pharmacists
- Statisticians
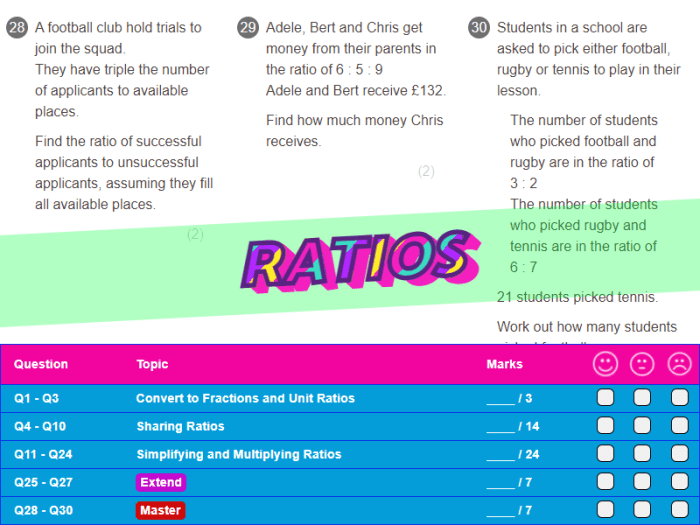
Practice and Review
This section provides practice problems and review questions to reinforce the concepts covered in Unit 2. Students should complete the assigned homework problems to solidify their understanding of ratios and their applications.
The practice problems cover a variety of exercises, including simplifying ratios, solving proportions, and applying ratios to real-world situations.
Practice Problems
- Simplify the ratio 12:18.
- Solve the proportion 3/5 = x/10.
- A recipe calls for 2 cups of flour to 3 cups of sugar. If you want to make half the recipe, how much flour and sugar will you need?
Review Questions
- What is a ratio?
- How do you simplify a ratio?
- How do you solve a proportion?
- Give an example of how ratios are used in real life.
Detailed FAQs: Unit 2 Introducing Ratios Answer Key
What are the different types of ratios?
Ratios can be classified into various types, including part-to-part ratios, part-to-whole ratios, and rate ratios.
How do I simplify a ratio?
To simplify a ratio, divide both the numerator and denominator by their greatest common factor (GCF).
What are the applications of ratios in real life?
Ratios find applications in numerous fields, including cooking, construction, finance, and scientific research.