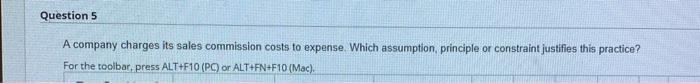
A company charges its sales commission costs to expense – A company’s decision to charge sales commission costs to expense has significant implications for its financial statements and overall financial performance. This comprehensive guide delves into the accounting treatment of sales commission costs, their impact on financial performance, and alternative accounting methods.
It also explores disclosure requirements and analyzes real-world case studies to provide a comprehensive understanding of this critical topic.
The subsequent paragraphs will provide detailed insights into the various aspects of expensing sales commission costs, offering valuable knowledge for accountants, financial analysts, and business professionals.
1. Accounting Treatment of Sales Commission Costs
Sales commission costs represent the compensation paid to salespeople based on their sales performance. The accounting treatment of these costs can vary depending on the company’s policies and the applicable accounting standards.
Expensing Sales Commission Costs
Expensing sales commission costs means recognizing them as an expense in the period in which they are incurred. This approach aligns with the matching principle, which states that expenses should be matched to the revenues they generate.
Capitalizing Sales Commission Costs
Capitalizing sales commission costs involves treating them as an asset on the balance sheet. This is typically done when the sales commissions are expected to generate future benefits that extend beyond the current period.
GAAP and IFRS, A company charges its sales commission costs to expense
- GAAP:Under GAAP, sales commission costs are generally expensed in the period incurred.
- IFRS:IFRS allows for both expensing and capitalizing sales commission costs, depending on the nature of the commissions.
Examples of Accounting for Sales Commission Costs
- Expensing:A company that pays sales commissions to its sales force on a monthly basis would typically expense these costs as incurred.
- Capitalizing:A company that incurs significant upfront sales commissions to acquire new customers may capitalize these costs and amortize them over the expected period of customer retention.
Questions and Answers: A Company Charges Its Sales Commission Costs To Expense
What is the difference between expensing and capitalizing sales commission costs?
Expensing sales commission costs recognizes them as an expense in the period incurred, while capitalizing them records them as an asset and amortizes them over the life of the related revenue.
How does expensing sales commission costs impact a company’s income statement?
Expensing sales commission costs reduces gross profit, operating profit, and net income in the period incurred.
What are the advantages of deferring sales commission costs?
Deferring sales commission costs can smooth earnings over multiple periods and reduce volatility in financial performance.