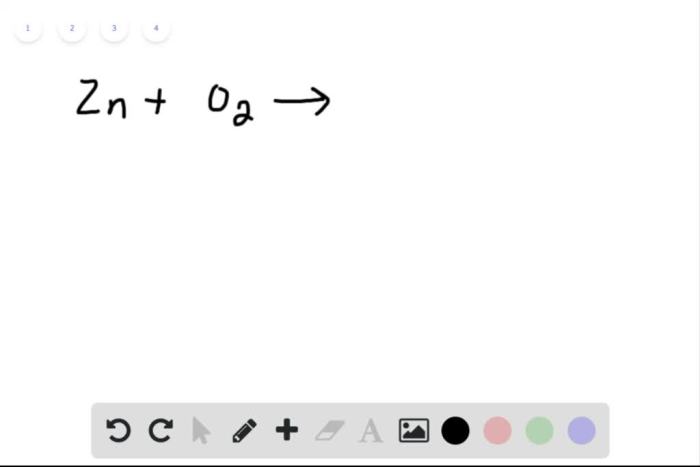
Balance the equation by inserting coefficients as needed. – Balancing chemical equations by inserting coefficients is a crucial skill in chemistry. It ensures that the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side matches the number of atoms of the same element on the products’ side. This introductory paragraph provides a captivating overview of the topic, setting the stage for a comprehensive exploration of the subject.
The subsequent paragraphs delve into the detailed steps involved in balancing equations, exploring methods such as the oxidation-reduction and half-reaction methods. Examples and applications of balanced equations are also discussed, highlighting their significance in stoichiometry and quantitative chemical analysis.
Balancing Chemical Equations
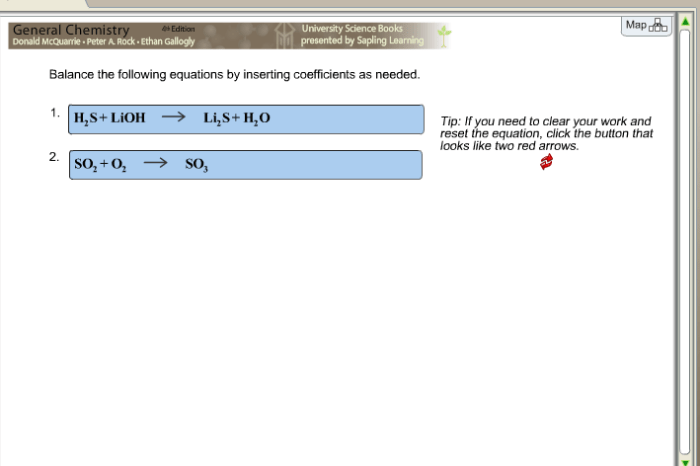
Balancing chemical equations involves adjusting the coefficients of reactants and products to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This ensures that the law of conservation of mass is upheld.
An unbalanced equation is one in which the number of atoms of each element is not the same on both sides. A balanced equation is one in which the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
Balancing equations is important in chemistry because it allows us to determine the stoichiometry of reactions, which is the quantitative relationship between the reactants and products.
Steps for Balancing Equations, Balance the equation by inserting coefficients as needed.
- Identify the reactants and products in the equation.
- Count the number of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
- Adjust the coefficients of the reactants and products until the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
Methods for Balancing Equations
There are two main methods for balancing equations: the oxidation-reduction method and the half-reaction method.
The oxidation-reduction method is based on the principle that the total number of electrons lost must be equal to the total number of electrons gained.
The half-reaction method is based on the principle that each half-reaction must be balanced in terms of mass and charge.
Examples of Balancing Equations
- Unbalanced equation: 2H2 + O2 → H2O
- Balanced equation: 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
Applications of Balanced Equations
Balanced chemical equations are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Stoichiometry
- Quantitative chemical analysis
- Thermochemistry
FAQ Guide: Balance The Equation By Inserting Coefficients As Needed.
What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element on the reactants’ side matches the number of atoms of the same element on the products’ side, representing the conservation of mass in chemical reactions.
What are the different methods for balancing chemical equations?
Common methods for balancing chemical equations include the oxidation-reduction method and the half-reaction method, both of which involve adjusting coefficients to achieve atom balance on both sides of the equation.
How are balanced chemical equations used in stoichiometry?
Balanced chemical equations provide the mole ratios of reactants and products, which are essential for quantitative analysis and determining the amounts of substances involved in chemical reactions.


![Rank the solutions in order of decreasing [h3o+] .](https://joan.perka.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/507/2024/05/779b3c8aea5932ebfdf83f20f6f636ae.jpg)
