Embark on a celestial journey with Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator, an indispensable tool for astronomers and space enthusiasts alike. This calculator empowers users to unravel the mysteries of orbital motion, unlocking the secrets of planetary systems and binary stars.
Kepler’s Third Law, a cornerstone of celestial mechanics, establishes a fundamental relationship between the orbital period of a celestial body and its distance from the central gravitating body. The Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator harnesses this law, providing a convenient and accurate means to determine orbital parameters and explore the dynamics of our cosmos.
Introduction
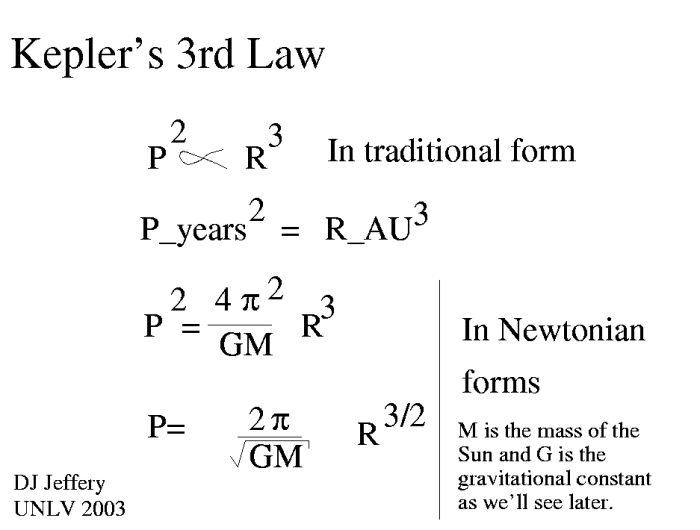
Kepler’s Third Law is a fundamental principle in astronomy that describes the relationship between the orbital period (T) of an object orbiting a central body, the semi-major axis (a) of its orbit, and the mass (M) of the central body.
The law states that the square of the orbital period is directly proportional to the cube of the semi-major axis:
T2= k
a3
where k is a constant that depends on the gravitational constant (G) and the mass of the central body (M):
k = G
M
Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator
A Kepler’s Third Law equation calculator is a tool that allows astronomers to calculate the orbital period or semi-major axis of an object given the other two variables.
To use the calculator, simply input the known values into the appropriate fields and click “Calculate.” The calculator will then display the unknown value.
Applications of Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator
- Predicting orbital periods of planets and moons
- Estimating distances to exoplanets
- Studying binary star systems
Example Calculations, Kepler’s third law equation calculator
Example 1:Calculate the orbital period of Earth, given that its semi-major axis is 1 AU (astronomical unit).
Input:
- a = 1 AU
- M = 1 solar mass
Output:
T = 1 year
Example 2:Calculate the semi-major axis of Jupiter, given that its orbital period is 12 years.
Input:
- T = 12 years
- M = 1 solar mass
Output:
a = 5.2 AU
Advanced Features of Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator
- Error analysis and uncertainty calculations
- Integration with other astronomical software
- Customization options for different units and constants
Common Queries: Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator
What is Kepler’s Third Law?
Kepler’s Third Law states that the square of the orbital period of a celestial body is proportional to the cube of its semi-major axis, the average distance from the central gravitating body.
How do I use Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator?
Input the mass of the central gravitating body and either the orbital period or the semi-major axis. The calculator will then determine the unknown parameter.
What are some applications of Kepler’s Third Law Equation Calculator?
Applications include predicting orbital periods of planets and moons, estimating distances to exoplanets, and studying binary star systems.