Photosynthesis what’s in a leaf answer key pdf – Delving into the intricacies of photosynthesis, this comprehensive guide unravels the secrets of nature’s life-sustaining process. Beginning with the fundamentals of photosynthesis, we explore the remarkable role of chloroplasts, the intricate anatomy of leaves, and the environmental factors that influence this vital process.
Prepare to delve into the world of photosynthesis, where sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide converge to create the very essence of life.
Unveiling the mechanisms that drive photosynthesis, this guide unveils the intricate dance between light-dependent and light-independent reactions. Witness the remarkable adaptations of leaves, maximizing their photosynthetic efficiency. Discover the profound impact of photosynthesis on our planet, serving as the cornerstone of food production, oxygen generation, and climate regulation.
Join us on this journey as we unlock the mysteries of photosynthesis, empowering you with a deeper understanding of this fundamental process.
1. Understanding Photosynthesis
The Process
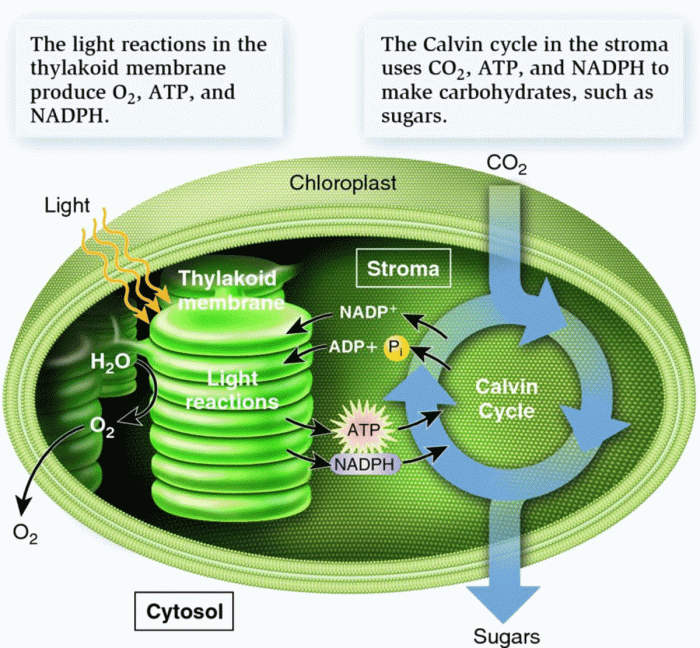
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process by which plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose. This process is crucial for life on Earth, as it provides the primary source of food and oxygen for most living organisms.
The photosynthesis process can be summarized as follows:
- Light energy is absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments in chloroplasts.
- The energy is used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- The hydrogen is used to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose.
- The oxygen is released as a byproduct.
Photosynthesis is performed by a wide range of organisms, including plants, algae, and certain bacteria. These organisms are known as photoautotrophs, meaning they can synthesize their own food from inorganic compounds using light energy.
2. The Role of Chloroplasts
Photosynthesis’s Powerhouse
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis. They contain chlorophyll and other pigments that absorb light energy, as well as the enzymes necessary for the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis.
The light-dependent reactions occur in the thylakoid membranes of chloroplasts and involve the conversion of light energy into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, occur in the stroma of chloroplasts and use the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions to reduce carbon dioxide into glucose.
3. The Leaf’s Anatomy
A Photosynthesis Factory
Leaves are the primary organs of photosynthesis in plants. They have a specialized structure that optimizes the absorption of light and the exchange of gases necessary for photosynthesis.
The leaf is composed of several layers of cells, including the epidermis, mesophyll, and vascular tissues. The epidermis is the outermost layer of cells and protects the leaf from water loss and mechanical damage. The mesophyll is the middle layer of cells and contains the chloroplasts where photosynthesis occurs.
The vascular tissues transport water and nutrients to and from the leaf.
Leaves have a number of adaptations that enhance their ability to perform photosynthesis, such as their large surface area, thin structure, and the presence of stomata. Stomata are small pores on the leaf surface that allow for the exchange of gases between the leaf and the atmosphere.
4. Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
Environmental Influences
The rate of photosynthesis is influenced by a number of environmental factors, including light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration.
Light intensity is the most important factor affecting photosynthesis. The rate of photosynthesis increases as light intensity increases, until a plateau is reached. Temperature also affects the rate of photosynthesis, with the optimal temperature for photosynthesis varying among different plant species.
Carbon dioxide concentration is another important factor, with higher carbon dioxide concentrations leading to increased rates of photosynthesis.
In addition to these factors, other environmental factors can also affect photosynthesis, such as water availability, nutrient availability, and pollution.
FAQ Resource: Photosynthesis What’s In A Leaf Answer Key Pdf
What is the primary pigment involved in photosynthesis?
Chlorophyll
Where do the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis occur?
Thylakoid membranes
What is the role of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis?
Provides the carbon atoms for glucose synthesis
How does temperature affect photosynthesis?
Optimal temperature range varies among plant species, but extreme temperatures can inhibit the process
What are the applications of photosynthesis in biotechnology?
Genetic modification of crops to improve yield and resistance to pests and diseases