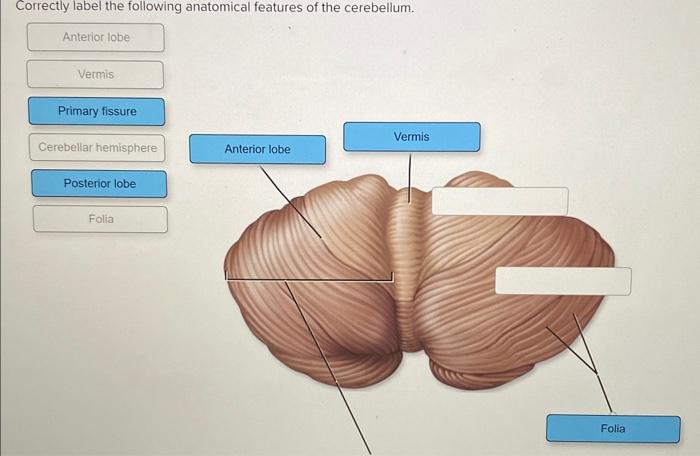
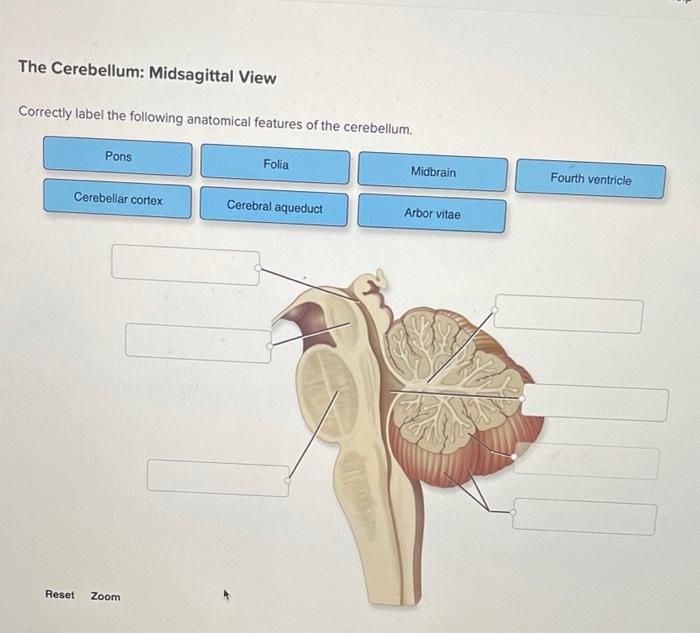
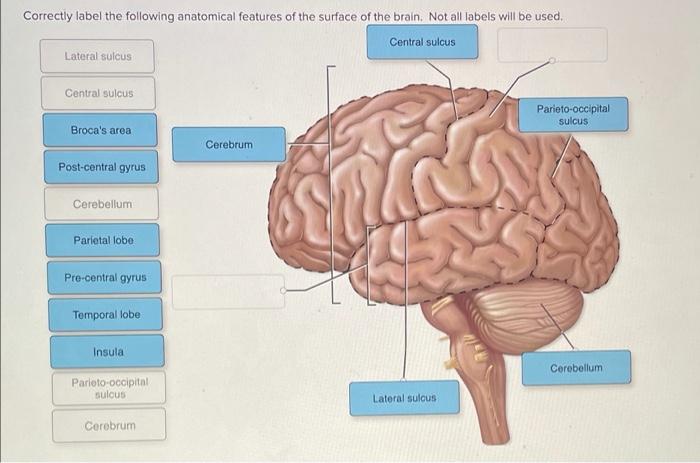
Correctly label the following anatomical features of the cerebellum. – Correctly labeling the anatomical features of the cerebellum is crucial for understanding its intricate structure and function. The cerebellum, located at the base of the brain, plays a pivotal role in motor coordination, balance, and cognitive processes. In this article, we will delve into the anatomical features of the cerebellum, exploring its vermis, hemispheres, lobes, and fissures, providing a comprehensive understanding of this vital brain region.
1. Anatomical Features of the Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a small but crucial structure located at the back of the brain, beneath the cerebrum. It plays a vital role in motor coordination, balance, and posture. The cerebellum is divided into two hemispheres, which are connected by a central structure called the vermis.
Each hemisphere is further divided into three lobes: the anterior lobe, posterior lobe, and flocculonodular lobe.The cerebellum is composed of several distinct anatomical features, including:
- Vermis:The vermis is a thin, midline structure that separates the two cerebellar hemispheres. It is responsible for coordinating movements between the two sides of the body.
- Hemispheres:The cerebellar hemispheres are located on either side of the vermis. They are responsible for controlling movement on the same side of the body.
- Lobes:The cerebellum is divided into three lobes: the anterior lobe, posterior lobe, and flocculonodular lobe. The anterior lobe is responsible for controlling eye movements, while the posterior lobe is responsible for coordinating limb movements. The flocculonodular lobe is responsible for maintaining balance.
- Fissures:The cerebellum is divided into several fissures, which are grooves that separate the different lobes and hemispheres. The most prominent fissure is the primary fissure, which separates the anterior lobe from the posterior lobe.
2. Functional Regions of the Cerebellum
The cerebellum is divided into three main functional regions:
- Vestibulocerebellum (Flocculonodular Lobe):The vestibulocerebellum is responsible for maintaining balance and coordinating eye movements with head movements.
- Spinocerebellum (Posterior Lobe):The spinocerebellum is responsible for coordinating limb movements and posture.
- Cerebrocerebellum (Anterior Lobe):The cerebrocerebellum is responsible for planning and executing complex movements, such as reaching and grasping.
The cerebellum receives input from various sensory systems, including the vestibular system, proprioceptive system, and visual system. It also receives input from the cerebral cortex. The cerebellum then integrates this information to generate motor commands that are sent to the brainstem and spinal cord.
3. Clinical Significance of the Cerebellum: Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Cerebellum.
Damage to the cerebellum can result in a variety of symptoms, including:
- Ataxia:Ataxia is a movement disorder that is characterized by difficulty with coordination and balance.
- Dysmetria:Dysmetria is a movement disorder that is characterized by difficulty with reaching and grasping objects.
- Nystagmus:Nystagmus is a condition that is characterized by involuntary eye movements.
- Tremor:Tremor is a condition that is characterized by involuntary shaking.
Cerebellar damage can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Stroke:A stroke is a sudden loss of blood flow to the brain. Strokes can damage the cerebellum and cause ataxia, dysmetria, nystagmus, and tremor.
- Traumatic brain injury:A traumatic brain injury is a head injury that can damage the cerebellum and cause ataxia, dysmetria, nystagmus, and tremor.
- Tumors:Tumors can grow in the cerebellum and cause ataxia, dysmetria, nystagmus, and tremor.
- Cerebellar degeneration:Cerebellar degeneration is a group of diseases that cause the cerebellum to deteriorate over time. Cerebellar degeneration can cause ataxia, dysmetria, nystagmus, and tremor.
4. Diagnostic Imaging of the Cerebellum
There are a variety of imaging techniques that can be used to visualize the cerebellum, including:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain. MRI can be used to diagnose cerebellar damage, such as tumors, strokes, and cerebellar degeneration.
- Computed tomography (CT):CT is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the brain. CT can be used to diagnose cerebellar damage, such as tumors and strokes.
- Positron emission tomography (PET):PET is a non-invasive imaging technique that uses radioactive tracers to measure metabolic activity in the brain. PET can be used to diagnose cerebellar damage, such as cerebellar degeneration.
Imaging can help diagnose cerebellar disorders by revealing abnormalities in the structure and function of the cerebellum.
Detailed FAQs
What is the function of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum plays a crucial role in motor coordination, balance, and cognitive functions such as attention and language.
What are the main anatomical features of the cerebellum?
The cerebellum comprises two hemispheres, separated by the vermis, and is divided into lobes and fissures.